Cousins in Binary Tree
Created: May 7, 2020 by [lek-tin]
Last updated: May 7, 2020
In a binary tree, the root node is at depth 0, and children of each depth k node are at depth k+1.
Two nodes of a binary tree are cousins if they have the same depth, but have different parents.
We are given the root of a binary tree with unique values, and the values x and y of two different nodes in the tree.
Return true if and only if the nodes corresponding to the values x and y are cousins.
Example 1:
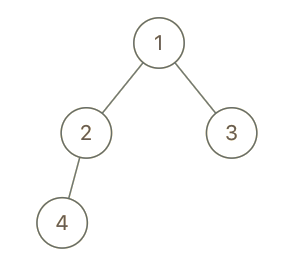
Input: root = [1,2,3,4], x = 4, y = 3
Output: false
Example 2:
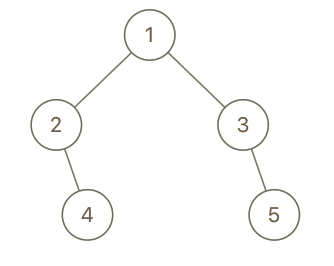
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4,null,5], x = 5, y = 4
Output: true
Example 3:
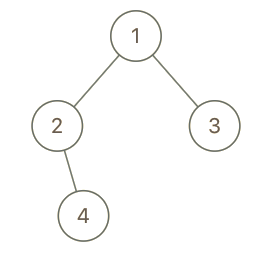
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4], x = 2, y = 3
Output: false
Note:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be between
2and100. - Each node has a unique integer value from
1to100.
Solution
Java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
boolean shared_parent = false;
int x_level = -1;
int y_level = -1;
public boolean isCousins(TreeNode root, int x, int y) {
dfs(root, x, y, 0);
System.out.println(shared_parent);
if (x_level > 0 && y_level > 0 && x_level == y_level && !shared_parent) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int x, int y, int level) {
if (root == null) return;
// early stop
if (shared_parent) return;
if (x_level > 0 && y_level > 0 && x_level != y_level) return
if (root.val == x) {
x_level = level;
return;
}
if (root.val == y) {
y_level = level;
return;
}
if (root.left != null && root.right != null) {
System.out.println(root.left.val + ", " + root.right.val);
if ( (root.left.val == x && root.right.val == y) ||
(root.left.val == y && root.right.val == x)
) {
shared_parent = true;
return;
}
}
dfs(root.left, x, y, level+1);
dfs(root.right, x, y, level+1);
}
}