Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
Created: February 27, 2020 by [lek-tin]
Last updated: February 27, 2020
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
Example 1
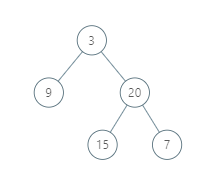
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0):
Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1);
The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2);
The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1);
The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme.
However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note
- The tree will have between
1 and 1000nodes. - Each node’s value will be between
0 and 1000.
Solution
Time: O(NlogN)
Space: O(N)
Nodes stored into list: lookup[col][row]
class Solution:
def verticalTraversal(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
def dfs(node, lookup, col, row):
if not node:
return
lookup[col][row].append(node)
dfs(node.left, lookup, col-1, row+1)
dfs(node.right, lookup, col+1, row+1)
# lookup shape:
# {
# int: {
# int: []
# }
# }
lookup = collections.defaultdict(lambda: collections.defaultdict(list))
dfs(root, lookup, 0, 0)
result = []
for col in sorted(lookup):
vertical = []
for row in sorted(lookup[col]):
print("col:", col, "row:", row)
# find which node comes above vertically
vertical.extend(sorted(node.val for node in lookup[col][row]))
result.append(vertical)
print("------")
return result